What is the meaning of stonemasonry?
Introduction
Stonemasonry is an ancient craft that involves the shaping, cutting, and laying of stones to create structures, sculptures, and decorative pieces. It is a skilled trade that has been practiced for centuries, with its origins dating back to the earliest civilizations. Stonemasons, also known as stone cutters or stone crafters, use various techniques and tools to work with stone materials and create beautiful and durable structures.
The Art and Craft of Stonemasonry
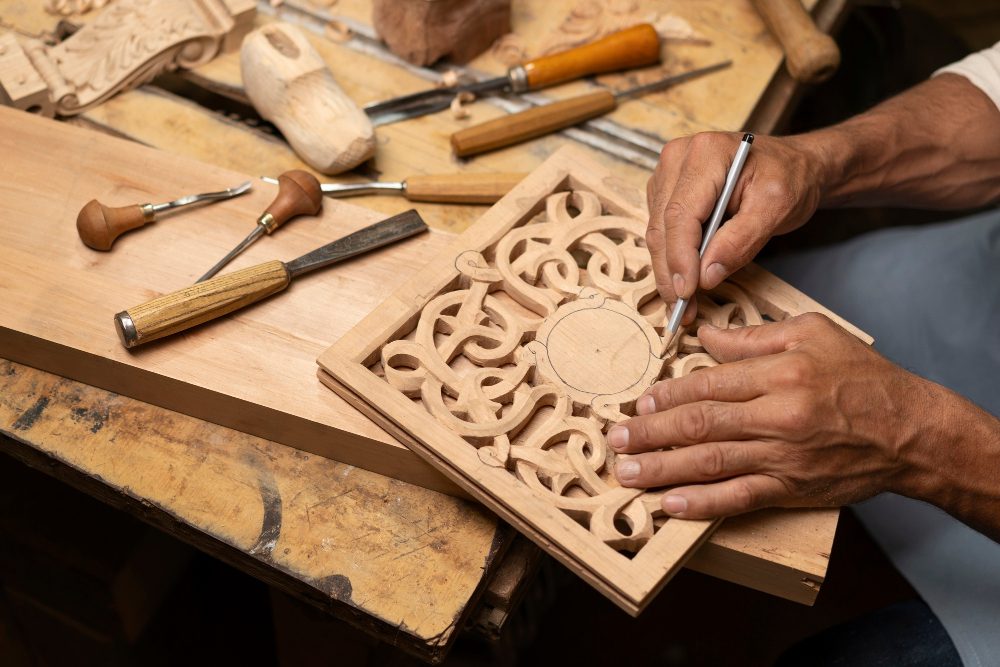
Stonemasonry is both an art and a craft, requiring a combination of artistic vision and technical skill. The process begins with the selection of suitable stones, which can vary in type, shape, and size depending on the desired outcome. The stones are then shaped, often using traditional hand tools such as chisels and hammers, to achieve the desired design.
Stonemasonry requires precision and attention to detail, as each stone must be carefully shaped and fitted together to create a structurally sound and aesthetically pleasing result. The mason must have a deep understanding of the properties of different types of stone, as well as the ability to work with the natural characteristics of each individual piece.
The History of Stonemasonry
Stonemasonry has a rich history that spans across continents and civilizations. From the ancient pyramids of Egypt to the towering cathedrals of Europe, stonemasonry has played a vital role in the construction of some of the world’s most iconic structures.
“The skill and craftsmanship of stonemasons can be seen in the intricate carvings, detailed sculptures, and elaborate architectural features that adorn many historical buildings.”
In medieval Europe, stonemasons formed guilds, which served as both professional associations and training institutions. These guilds provided apprenticeships and training for aspiring stonemasons, ensuring the passing down of knowledge and techniques from one generation to another.
The Role of Stonemasonry Today
While the demand for traditional stonemasonry has decreased with the advent of modern construction materials and techniques, it still holds a special place in contemporary architecture and restoration projects. Stonemasonry is often used to preserve and restore historical buildings, ensuring that their original beauty and integrity are maintained.
“Stonemasonry is a craft that connects us to our past, allowing us to appreciate the skilled workmanship of previous generations.”
Today, stonemasons may also work on new construction projects, incorporating the timeless elegance of stone into modern designs. The versatility and durability of stone make it a popular choice for various applications, including facades, flooring, fireplaces, and even outdoor landscaping.
What is Stone Masonry and its Types?
Stone masonry is a timeless construction technique that involves building structures using natural stones. It has been used for centuries to create durable and aesthetically pleasing buildings, monuments, and sculptures. The art of stone masonry requires skilled craftsmen who have a deep understanding of the properties of various types of stones and the techniques involved in cutting, shaping, and placing them.
Types of Stone Masonry
There are different types of stone masonry, each with its own unique characteristics and applications:
- Rubble Masonry: This type of stone masonry uses irregularly shaped stones of different sizes and shapes. The stones are laid together with mortar, leaving gaps between them. Rubble masonry is commonly used for foundations and walls where appearance is not the primary concern.
- Ashlar Masonry: In ashlar masonry, rectangular or square-cut stones are used. The stones are carefully cut and dressed to have flat surfaces and right angles, resulting in a neat and uniform appearance. Ashlar masonry is commonly used for building facades and prestigious structures.
- Coursed Masonry: This type of stone masonry involves arranging stones in courses or layers of equal height. The stones are shaped and cut to fit together tightly, creating a smooth and even surface. Coursed masonry is commonly used for load-bearing walls and retaining walls.
Stone masonry offers several advantages over other construction methods. Stones are naturally durable and resistant to weathering, making structures built with stone masonry long-lasting. Additionally, stone structures provide excellent thermal insulation and have a classic and timeless aesthetic appeal.
Did you know? The Great Wall of China, the Pyramids of Giza, and the Colosseum in Rome are all examples of remarkable stone masonry constructions.
Comparison of Stone Masonry Types
| Type of Stone Masonry | Appearance | Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Rubble Masonry | Irregular and rough | Foundations, boundary walls |
| Ashlar Masonry | Neat and uniform | Building facades, prestigious structures |
| Coursed Masonry | Smooth and even | Load-bearing walls, retaining walls |
Stone masonry continues to be an important craft in the UK, with many historic buildings showcasing the timeless beauty and durability of this construction method. Whether it’s a small garden wall or a grand cathedral, stone masonry adds a touch of elegance and permanence to any structure.
So, the next time you admire an old stone building, take a moment to appreciate the skill and craftsmanship of the stonemasons who brought it to life.