What is the profession of stone crafting called?
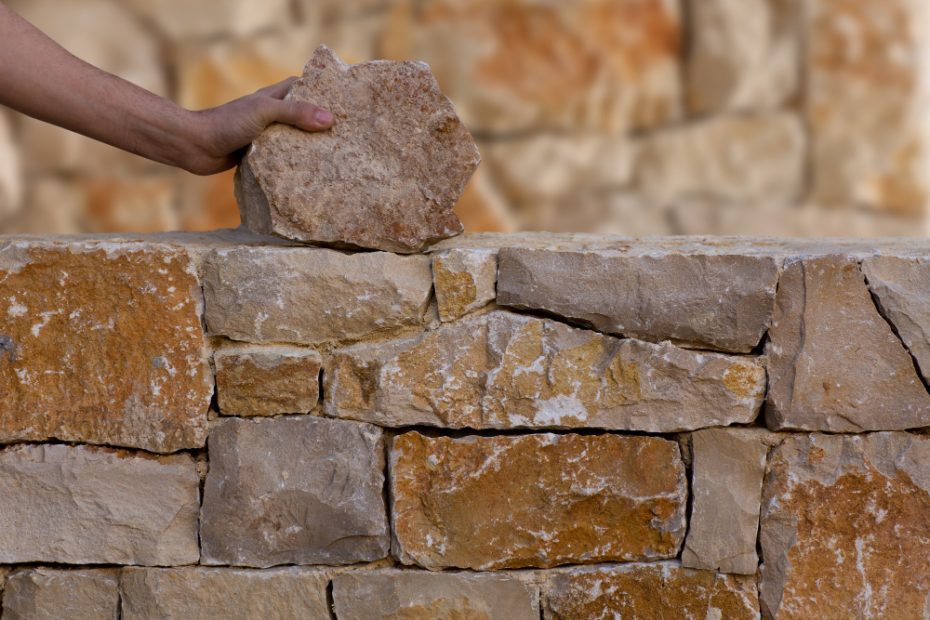
Stone crafting is an ancient and esteemed profession that involves transforming raw pieces of stone into beautiful and functional works of art. The individuals who practice this skill are known as stonecrafters or stonemasons. This noble profession has been in existence for centuries, with its roots dating back to ancient civilizations such as Egypt, Greece, and Rome.
The Art and Skill of Stone Crafting
Stone crafting requires a unique combination of artistic vision, technical expertise, and physical strength. It involves working with various types of stone, including granite, marble, limestone, and sandstone. Stonecrafters use specialized tools and techniques to shape and refine these natural materials, bringing out their inherent beauty and potential.
The Role of a Stonecrafter
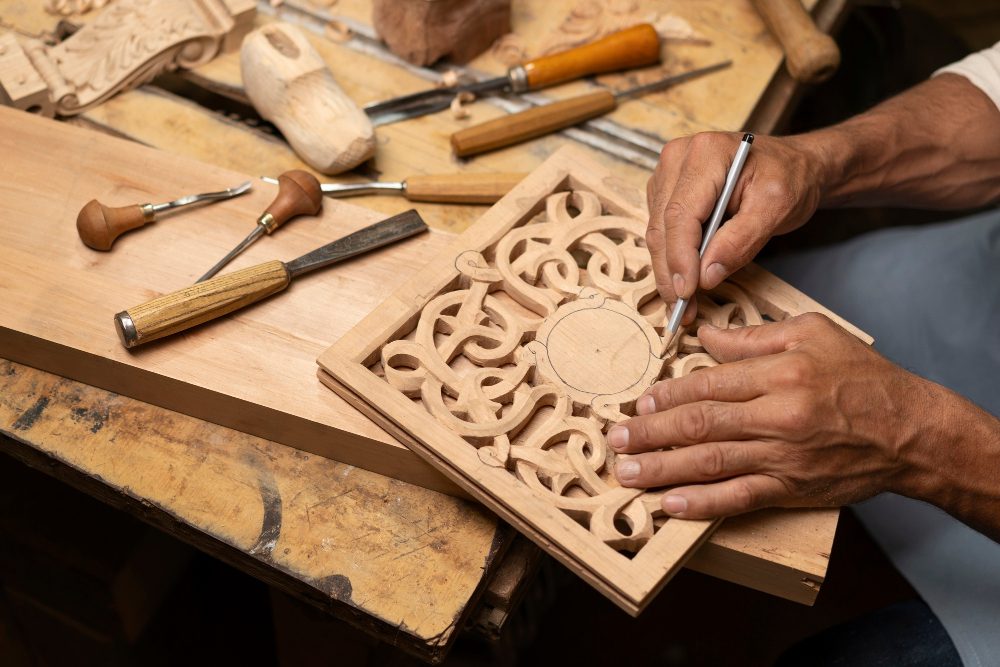
A stonecrafter’s primary role is to create and restore structures, sculptures, and other objects using stone as the medium. They work on a wide range of projects, from building historic monuments, religious structures, and public buildings to crafting intricate details like statues, engravings, and decorative elements. Their work often involves carving, cutting, polishing, and assembling stones to create visually stunning and durable creations.
The Training and Expertise
Becoming a proficient stonecrafter requires years of training and experience. Traditionally, apprentices would learn the craft through hands-on training under the guidance of skilled masters. Today, there are vocational schools and programs that offer formal education in stonecrafting, providing aspiring craftsmen with the necessary knowledge and techniques.
The Importance of Stonecrafting
Stonecrafting is not merely a profession; it is a vital part of our cultural heritage. Throughout history, stone has been a symbol of strength, endurance, and permanence. Stonecrafted structures have stood the test of time and serve as a testament to human ingenuity and craftsmanship. Stonecrafting plays a significant role in preserving our architectural heritage, restoring historical landmarks, and creating lasting works of art.
Stonecrafting is a blend of artistry, precision, and respect for tradition. It requires an understanding of the properties of different stones and the ability to transform them into objects that will withstand the test of time.
The Future of Stone Crafting
While stonecrafting remains deeply rooted in tradition, it has also embraced modern technologies and techniques. Advanced machinery, such as computer-aided design (CAD) and computer numerical control (CNC) machines, now augment the work of stonecrafters. These tools enable greater precision, efficiency, and the ability to take on more complex projects.
Challenges and Opportunities
The profession of stone crafting faces its own set of challenges and opportunities in the modern world. The demand for skilled stonecrafters continues to exist, particularly in restoration and preservation projects. However, the advent of prefabricated building materials and changing architectural trends poses some challenges. Adapting to new technologies and finding innovative ways to incorporate stone into contemporary designs will be crucial for future generations of stonecrafters.
Preserving a Rich Tradition
Despite these challenges, the profession of stone crafting is far from disappearing. Its timeless appeal and the unique beauty of stone ensure its relevance in our society. Preservation efforts, education, and the recognition of the value of skilled craftsmanship all contribute to the continuity of this proud profession.
In Conclusion
Stonecrafting is more than just a profession; it is a celebration of human creativity, skill, and heritage. The work of stonecrafters enriches our lives with stunning architectural masterpieces, cultural landmarks, and intricate sculptures that tell stories of our past. As we continue to appreciate and support the art of stone crafting, we ensure that this ancient profession will thrive and be passed down for future generations to admire and cherish.
What are some examples of stonemasonry?
Stone crafting, also known as stonemasonry, is a centuries-old profession that involves shaping and constructing structures using stone. Stonemasons have played a significant role in creating various architectural wonders around the world. Here are some notable examples of stonemasonry:
1. The Great Pyramids of Giza, Egypt
Built over 4,500 years ago, the Great Pyramids of Giza are a testament to the skill and precision of ancient Egyptian stonemasons. These magnificent structures were constructed using massive limestone blocks, weighing several tons each.
2. The Taj Mahal, India
Considered one of the world’s most beautiful buildings, the Taj Mahal showcases intricate stonemasonry. The white marble exterior is adorned with delicate carvings, showcasing the mastery of Indian stonemasons.
3. Stonehenge, United Kingdom
Stonehenge, a prehistoric monument located in Wiltshire, England, demonstrates the skill of Neolithic stonemasons. The large standing stones were meticulously shaped and arranged in a circular formation, representing an impressive feat of stonemasonry.
4. The Parthenon, Greece
The Parthenon, an ancient Greek temple, serves as a prime example of classical stonemasonry. The structure was constructed using carefully cut marble blocks and featured intricate decorative sculptures, showcasing Greek craftsmanship.
5. Chartres Cathedral, France
Chartres Cathedral, located in Chartres, France, is celebrated for its Gothic architecture and exceptional stonemasonry. The cathedral’s façade is adorned with elaborate stone carvings, while its interior showcases expertly crafted columns and arches.
Stonemasonry involves various techniques and styles, such as carving, shaping, and laying stones to create structures that withstand the test of time. It requires a combination of artistic vision, technical skill, and a deep understanding of the properties of different types of stone.
Stonemasonry is a profession that has shaped the world we live in. From ancient monuments to modern-day architectural marvels, the skill and craftsmanship of stonemasons continue to inspire awe. As Charles Rennie Mackintosh once said,
“There is no such thing as bad material; only bad craftsmen.”
In addition to these grand structures, stonemasonry can also be seen in smaller-scale projects such as sculptures, garden features, and ornamental pieces. It is a versatile profession that combines artistry with practicality.
To gain a better appreciation for stonemasonry, here is a comparison table showcasing different types of stones commonly used in this craft:
| Type of Stone | Properties | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Granite | Durable, resistant to heat and scratches | Countertops, monuments, building facades |
| Marble | Elegant appearance, easy to carve | Sculptures, flooring, decorative elements |
| Sandstone | Natural color variations, good weather resistance | Building exteriors, paving, garden features |
Whether it’s the sheer scale of an ancient pyramid or the delicate intricacy of a carved sculpture, stonemasonry is an art form that has stood the test of time. The profession continues to evolve, combining traditional techniques with modern innovations to create structures that capture both history and imagination.
- The Great Pyramids of Giza
- The Taj Mahal
- Stonehenge
- The Parthenon
- Chartres Cathedral
These are just a few examples of the incredible workmanship achieved by stonemasons throughout history. Their dedication and skill have left a lasting legacy, shaping the world’s architectural heritage for generations to come. Whether it’s a towering monument or a subtle detail, the art of stonemasonry continues to captivate and inspire.